Body-Contouring After Rapid Weight Loss: What Patients Need to Know
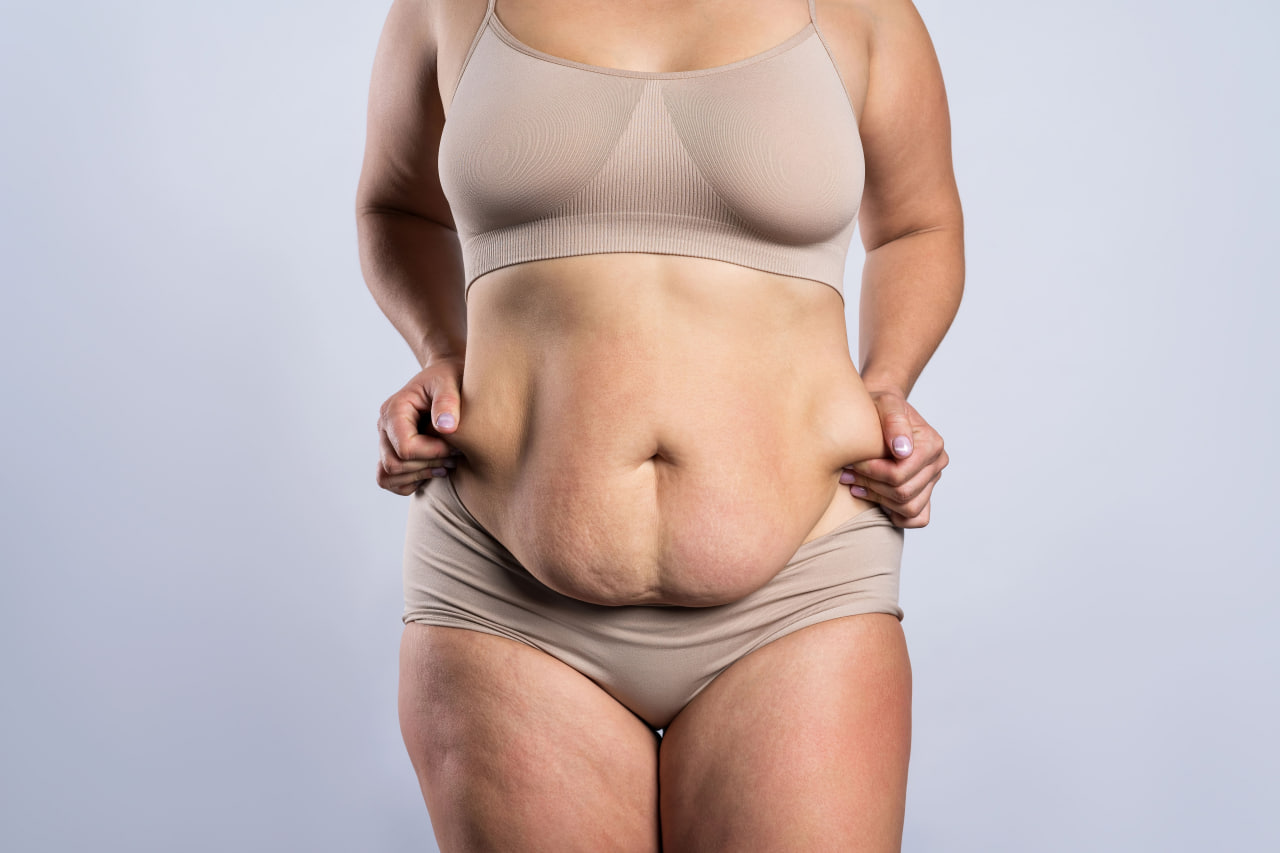
Rapid weight loss (through medications, diets, or bariatric surgery) often leads to excellent results. At the same time, one of the most common side effects is excess, sagging skin in different areas of the body. This can cause physical discomfort (chafing, rashes, hygiene difficulties), limit mobility, and significantly affect a patient’s psychosocial well-being. That is why demand is growing for body-contouring surgeries, including abdominoplasty, brachioplasty, thigh lifts, and other corrective procedures.
Why Excess Skin Remains After Weight Loss
Skin loses volume and elasticity during rapid fat reduction. The severity of this issue is usually influenced by:
- age (older patients have less elastic skin),
- duration of obesity (long-term stretching reduces the skin’s ability to retract),
- rate of weight loss (faster weight loss allows less time for adaptation).
Conservative methods (exercise, creams, massages) often fail to resolve excess skin, making plastic surgery the optimal solution. However, such procedures are performed only on patients who have already reached a stable, comfortable weight and do not plan further weight loss. Physicians generally recommend waiting at least 12–18 months after bariatric surgery and 3–6 months after weight stabilization.
It is important for patients to understand that body-contouring improves appearance but is not a method for additional weight reduction.
Main Types of Post-Weight Loss Surgeries
Here are the key procedures most commonly performed after significant weight loss, with a brief overview of when they are indicated and what to expect.
Abdominoplasty (Tummy Tuck) and Panniculectomy
- Abdominoplasty – combines removal of excess skin with correction of the musculoaponeurotic structure; most often performed as a cosmetic procedure in patients with stable weight.
- Panniculectomy – radical removal of the “apron” of skin and subcutaneous tissue, sometimes performed for medical reasons (hygiene problems, ulcerations).
In patients after massive weight loss, abdominoplasty carries a higher risk of complications (delayed wound healing, seromas) compared with cosmetic patients. This makes careful planning and thorough preparation critically important for achieving positive outcomes.

Thigh Lifts and Brachioplasty (Arm Contouring)
These procedures address excess skin on the inner thighs and sagging skin of the upper arms (typically in the triceps area). They are often performed as a second or third stage within a stepwise body-contouring plan.
Mastopexy and Breast Reduction
After significant weight loss, breasts tend to lose volume and sag. Mastopexy (with or without implants) addresses breast shape and position. The choice of technique depends on residual volume, proportions, and the patient’s preferences.
One Stage or Multiple?
Following massive weight loss, surgeons often prefer a staged approach: combining multiple large areas in a single operation can increase blood loss, complication risks, and anesthesia duration. For patients with comorbidities, it is advisable to divide contouring procedures into 2–4 stages spaced several months apart. The plan is tailored individually, considering overall health, the distribution of excess skin, and patient goals.
Recovery and Results
Recovery after major contouring surgeries typically lasts from several weeks up to six months. Patients usually require assistance during the first 1–2 weeks, must avoid intensive physical activity for 6–12 weeks, and should wear compression garments for 4–8 weeks.
Most patients need additional procedures or minor corrections within 6–12 months. When performed correctly, body-contouring surgeries significantly improve quality of life, self-esteem, and long-term weight stability for the majority of patients.
Conclusion
Body-contouring after rapid weight loss is the most effective way to eliminate excess skin and restore body shape. The best time to undergo surgery is once weight has stabilized, nutrition is well-balanced, and the patient is prepared for rehabilitation (typically 12–18 months after bariatric surgery or after weight stabilization).
Planning should be multidisciplinary and staged: the surgeon, bariatric specialist, nutritionist, and psychologist all play a role in ensuring a safe and sustainable outcome.
If you are considering body-contouring, I invite you to schedule a consultation. Together, we will create a safe, realistic, and personalized plan to restore the natural contours of your body.
Contact me
Plastic surgeon
Ukraine, Kyiv, Shchekavytska St., 9a
(Clinic "Nove Tilo")